Overview

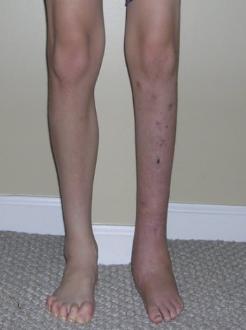
Flat feet can also develop as an adult ("adult acquired flatfoot") due to injury, illness, unusual or prolonged stress to the foot, faulty biomechanics or as part of the normal aging process. This is most common in women over 40 years of age. Known risk factors include obesity, hypertension and diabetes.Flat feet can also occur in pregnant women as a result of temporary changes, due to increased elastin (elasticity) during pregnancy. However, if developed by adulthood, flat feet generally remain flat permanently.
Causes
A fallen arch occurs because one of the main structures that support the arch has broken or torn. Usually it occurs without trauma, although a small injury associated with the onset of the pain is often recalled, it is sometimes difficult to determine whether the injury was clearly big enough to permanently injure the leg. I suspect that even before the symptoms that the structure that broke was weakening and the injury was simply the ?needle that broke the camels back?. The structure that is most commonly torn is the posterior tibial tendon. This tendon is attached to a muscle on the inside of the back of the ankle, and runs along the medial malleolus, the bony prominence on the inside of the ankle, to attach to a bone in the arch called the navicular bone. It usually begins to weaken and stretch along the back of the medial malleolus. It often begins as a swelling and the arch flattens over the next several weeks to months. As the arch flattens, other structures that support the arch begin to stretch and tear. The bones along the outside of the ankle begin to crush together, causing pain and swelling in this are, and the toes may tilt to the outside as the arch collapses. It is not known why this process begins. It is often associated with diabetes and rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory diseases. It also is more common as a person enters the fifty to seventy year age range. ?Fallen arches? are much more common in people who are already flat footed.
Symptoms
Flat feet can cause a myriad of symptoms, from experiencing pain in the foot, heels, arch, calves, the shin, the knee, the hip and into the lower back due to overworking of the hip flexors or they may find it hard to stand on tip toes.
Diagnosis
Your doctor examines your feet to determine two things, whether you have flat feet and the cause or causes. An exam may include the following steps, Checking your health history for evidence of illnesses or injuries that could be linked to flat feet or fallen arches, Looking at the soles of your shoes for unusual wear patterns, Observing the feet and legs as you stand and do simple movements, such as raising up on your toes, Testing the strength of muscles and tendons, including other tendons in the feet and legs, such as the Achilles tendon or the posterior tibial tendon, Taking X-rays or an MRI of your feet.
pes planus radiology
Non Surgical Treatment
If you have flat feet, you may also experience pain throughout the lower body and into the lower back. Orthotics (custom-made rigid foot supports) can be prescribed when over-the-counter supports do not provide releif and surgery can also offer a more permanent solution in severe cases. The board-certified doctors in our practice would be able to select the most appropriate course of action in each case.
Surgical Treatment

Fallen arches may occur with deformities of the foot bones. Tarsal coalition is a congenital condition in which the bones of the foot do not separate from one another during development in the womb. A child with tarsal coalition exhibits a rigid flat foot, which can be painful, notes the patient information website eOrthopod. Surgery may prove necessary to separate the bones. Other foot and ankle conditions that cause fallen arches may also require surgery if noninvasive treatments fail to alleviate pain and restore normal function.
Prevention
Flat feet or Fallen Arches cannot be prevented due to congenital of nature or from underlying disease process; however, painful symptoms and future pathology from Flat Feet or Fallen Arches may be prevented by the following. Continue to wear your orthotics for work and exercise to provide stability and maintain function of your feet. Footwear. Continue to wear supportive shoes to maximise the function of your orthotic and prevent excessive movement of the joints in your feet.
After Care
Time off work depends on the type of work as well as the surgical procedures performed. . A patient will be required to be non-weight bearing in a cast or splint and use crutches for four to twelve weeks. Usually a patient can return to work in one to two weeks if they are able to work while seated. If a person's job requires standing and walking, return to work may take several weeks. Complete recovery may take six months to a full year. Complications can occur as with all surgeries, but are minimized by strictly following your surgeon's post-operative instructions. The main complications include infection, bone that is slow to heal or does not heal, progression or reoccurrence of deformity, a stiff foot, and the need for further surgery. Many of the above complications can be avoided by only putting weight on the operative foot when allowed by your surgeon.

Flat feet can also develop as an adult ("adult acquired flatfoot") due to injury, illness, unusual or prolonged stress to the foot, faulty biomechanics or as part of the normal aging process. This is most common in women over 40 years of age. Known risk factors include obesity, hypertension and diabetes.Flat feet can also occur in pregnant women as a result of temporary changes, due to increased elastin (elasticity) during pregnancy. However, if developed by adulthood, flat feet generally remain flat permanently.
Causes
A fallen arch occurs because one of the main structures that support the arch has broken or torn. Usually it occurs without trauma, although a small injury associated with the onset of the pain is often recalled, it is sometimes difficult to determine whether the injury was clearly big enough to permanently injure the leg. I suspect that even before the symptoms that the structure that broke was weakening and the injury was simply the ?needle that broke the camels back?. The structure that is most commonly torn is the posterior tibial tendon. This tendon is attached to a muscle on the inside of the back of the ankle, and runs along the medial malleolus, the bony prominence on the inside of the ankle, to attach to a bone in the arch called the navicular bone. It usually begins to weaken and stretch along the back of the medial malleolus. It often begins as a swelling and the arch flattens over the next several weeks to months. As the arch flattens, other structures that support the arch begin to stretch and tear. The bones along the outside of the ankle begin to crush together, causing pain and swelling in this are, and the toes may tilt to the outside as the arch collapses. It is not known why this process begins. It is often associated with diabetes and rheumatoid arthritis and other inflammatory diseases. It also is more common as a person enters the fifty to seventy year age range. ?Fallen arches? are much more common in people who are already flat footed.
Symptoms
Flat feet can cause a myriad of symptoms, from experiencing pain in the foot, heels, arch, calves, the shin, the knee, the hip and into the lower back due to overworking of the hip flexors or they may find it hard to stand on tip toes.
Diagnosis
Your doctor examines your feet to determine two things, whether you have flat feet and the cause or causes. An exam may include the following steps, Checking your health history for evidence of illnesses or injuries that could be linked to flat feet or fallen arches, Looking at the soles of your shoes for unusual wear patterns, Observing the feet and legs as you stand and do simple movements, such as raising up on your toes, Testing the strength of muscles and tendons, including other tendons in the feet and legs, such as the Achilles tendon or the posterior tibial tendon, Taking X-rays or an MRI of your feet.
pes planus radiology
Non Surgical Treatment
If you have flat feet, you may also experience pain throughout the lower body and into the lower back. Orthotics (custom-made rigid foot supports) can be prescribed when over-the-counter supports do not provide releif and surgery can also offer a more permanent solution in severe cases. The board-certified doctors in our practice would be able to select the most appropriate course of action in each case.
Surgical Treatment

Fallen arches may occur with deformities of the foot bones. Tarsal coalition is a congenital condition in which the bones of the foot do not separate from one another during development in the womb. A child with tarsal coalition exhibits a rigid flat foot, which can be painful, notes the patient information website eOrthopod. Surgery may prove necessary to separate the bones. Other foot and ankle conditions that cause fallen arches may also require surgery if noninvasive treatments fail to alleviate pain and restore normal function.
Prevention
Flat feet or Fallen Arches cannot be prevented due to congenital of nature or from underlying disease process; however, painful symptoms and future pathology from Flat Feet or Fallen Arches may be prevented by the following. Continue to wear your orthotics for work and exercise to provide stability and maintain function of your feet. Footwear. Continue to wear supportive shoes to maximise the function of your orthotic and prevent excessive movement of the joints in your feet.
After Care
Time off work depends on the type of work as well as the surgical procedures performed. . A patient will be required to be non-weight bearing in a cast or splint and use crutches for four to twelve weeks. Usually a patient can return to work in one to two weeks if they are able to work while seated. If a person's job requires standing and walking, return to work may take several weeks. Complete recovery may take six months to a full year. Complications can occur as with all surgeries, but are minimized by strictly following your surgeon's post-operative instructions. The main complications include infection, bone that is slow to heal or does not heal, progression or reoccurrence of deformity, a stiff foot, and the need for further surgery. Many of the above complications can be avoided by only putting weight on the operative foot when allowed by your surgeon.



 Morton's Neuroma is a common foot problem associated with pain, swelling and/or an inflammation of a nerve, usually at the ball-of-the-foot between the 3rd and 4th toes. Symptoms of this condition include sharp pain, burning, and even a lack of feeling in the affected area. Morton's Neuroma may also cause numbness, tingling, or cramping in the forefoot.
Morton's Neuroma is a common foot problem associated with pain, swelling and/or an inflammation of a nerve, usually at the ball-of-the-foot between the 3rd and 4th toes. Symptoms of this condition include sharp pain, burning, and even a lack of feeling in the affected area. Morton's Neuroma may also cause numbness, tingling, or cramping in the forefoot.












 RSS Feed
RSS Feed
